Complicações neurovasculares em fraturas supracondilianas de úmero em crianças
Conteúdo do artigo principal
Resumo
Introdução: As fraturas da porção supracondiliana do úmero são muito frequentes na população pediátrica, cujo mecanismo de trauma principal é a queda com o apoio das mãos e cotovelo estendido. O tratamento visa reestabelecer a posição correta da articulação e evitar complicações, em especial neurovasculares,
Objetivos: Analisar o perfil epidemiológico dessas fraturas correlacionando-as com complicações neurovasculares.
Método: Estudo individuado transversal observacional e descritivo, com amostra de 172 prontuários de crianças com fraturas supracondilianas de úmero. Estudaram-se variáveis demográficas, classificação, tratamento realizado, tempo de internamento hospitalar e se houve ou não complicação neurovascular.
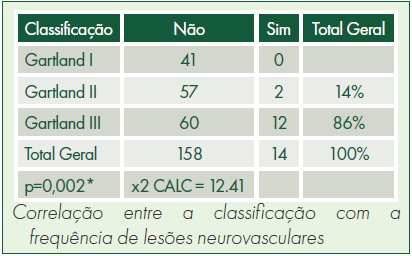
Resultados: A idade média dos pacientes no momento da fratura foi aos 5 anos. As complicações neurovasculares mais relevantes foram naqueles em Gartland mais avançado e atingindo com maior frequência o nervo radial. Foram 86% em pacientes Gartland III e 14% em Gartland II.
Conclusão: Lesões neurovasculares foram predominantemente observadas em fraturas Gartland III, caracterizadas por maior desvio. O nervo radial e artéria braquial foram os mais afetados. Em relação ao tratamento, a abordagem cirúrgica foi mais prevalente do que o tratamento conservador. O perfil epidemiológico dessas fraturas em crianças demonstrou ser heterogêneo.
Detalhes do artigo

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Referências
Chin K, Hussain S, Mazis G, Arya A. Clinical anatomy and biomechanics of the elbow. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;20:101485. Doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2021.101485
Kropelnicki A, Ali AM, Popat R, Sarraf KM. Paediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2019;80(6):312-6. Doi: 10.12968/hmed.2019.80.6.312
Poggiali P, Nogueira FCS, Nogueira MP de M. Manejo da fratura supracondiliana do úmero na criança. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia. 2020;57(1):23-32. Doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1709734
Omid R, Choi PD, Skaggs DL. Supracondylar Humeral Fractures in Children. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume. 2008;90(5):1121–32. Doi:10.2106/jbjs.g.01354
Holt JB, Glass NA, Shah AS. Understanding the Epidemiology of Pediatric Supracondylar Humeral Fractures in the United States: Identifying Opportunities for Intervention. J Pediatr Orthop. 2018;38(5):e245–51. Doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001154
Pilla NI, Rinaldi J, Hatch M, Hennrikus W. Epidemiological Analysis of Displaced Supracondylar Fractures. Cureus. 2020;12(4):e7734. Doi:10.7759/cureus.7734
Farnsworth C, Silva P, Mubarak S. Etiology of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 1998;18(1):38-42.
Leitch KK, Kay RM, Femino JD, Tolo VT, Storer SK, Skaggs DL. Treatment of multidirectionally unstable supracondylar humeral fractures in children. A modified Gartland type-IV fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;88(5):980-5. Doi: 10.2106/JBJS.D.02956
Martini RK, Fonseca GF, Martini RK, Azeredo Filho M, Serafini OA. Análise de fraturas supracondilianas do úmero em crianças. Acta Ortop Bras. 2002;10(2):25-30. Doi: 10.1590/S1413-78522002000200004
Anjum R, Sharma V, Jindal R, Singh TP, Rathee N. Epidemiologic pattern of paediatric supracondylar fractures of humerus in a teaching hospital of rural India: A prospective study of 263 cases. Chin J Traumatol. 2017;20(3):158-60. Doi:10.1016/j.cjtee.2016.10.007
Martínez JLA, Almero LP, de Anda RMCO, Botaya EG, Montolio MG, Rey MFM. Epidemiological study on supracondylar fractures of distal humerus in pediatric patients. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2019;63(6):394-9. Doi: 10.1016/j.recot.2019.07.001
Shore BJ, Gillespie BT, Miller PE, Bae DS, Waters PM. Recovery of Motor Nerve Injuries Associated With Displaced, Extension-type Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2019;39(9):e652-6. Doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001056
Babal JC, Mehlman CT, Klein G. Nerve injuries associated with pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures: a meta-analysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(3):253-63. Doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181d213a6
Howard A, Mulpuri K, Abel MF, Braun S, Bueche M, Epps H, et al. The treatment of pediatric supracondylar humerus fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):320-7. Doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-05-320
Tomaszewski R, Pethe K, Kler J, Rutz E, Mayr J, Dajka J. Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus: Association of Neurovascular Lesions with Degree of Fracture Displacement in Children - A Retrospective Study. Children. 2022;9(3):308. Doi:10.3390/children9030308
Choi PD, Melikian R, Skaggs DL. Risk Factors for Vascular Repair and Compartment Syndrome in the Pulseless Supracondylar Humerus Fracture in Children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010;30(1):50-6. Doi:10.1097/bpo.0b013e318
Badkoobehi H, Choi PD, Bae DS, Skaggs DL. Management of the Pulseless Pediatric Supracondylar Humeral Fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(11):937-43. Doi:10.2106/jbjs.n.00983
Ramachandran M, Birch R, Eastwood DM. Clinical outcome of nerve injuries associated with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children: the experience of a specialist referral centre. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(1):90-4. Doi:10.1302/0301-620x.88b1.16869
Valencia M, Moraleda L, Díez-Sebastián J. Long-term Functional Results of Neurological Complications of Pediatric Humeral Supracondylar Fractures. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2015;35(6):606-10. Doi:10.1097/bpo.0000000000000337
Matuszewski Ł. Evaluation and management of pulseless pink/pale hand syndrome coexisting with supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(8):1401-6. Doi:10.1007/s00590-013-1337-4
Alton TB, Werner SE, Gee AO. Classifications In Brief: The Gartland Classification of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;473(2):738–41. Doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-4033-8
Mulpuri K, Wilkins K. The treatment of displaced supracondylar humerus fractures: evidence-based guideline. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012;32(Suppl 2):S143-52. Doi:10.1097/BPO.0b013e318255b17b
Joiner ERA, Skaggs DL, Arkader A, Andras LM, Lightdale-Miric NR, Pace JL, et al. Iatrogenic nerve injuries in the treatment of supracondylar humerus fractures: are we really just missing nerve injuries on preoperative examination? J Pediatr Orthop. 2014;34(4):388-92. Doi:10.1097/BPO.0000000000000171
Cramer KE, Green NE, Devito DP. Incidence of anterior interosseous nerve palsy in supracondylar humerus fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1993;13(4):502-5. Doi:10.1097/01241398-199307000-00015
Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58(4):453-8.
Battle J, Carmichael KD. Incidence of Pin Track Infections in Children’s Fractures Treated With Kirschner Wire Fixation. J Pediatr Orthop. 2007;27(2):154-7. Doi:10.1097/bpo.0b013e3180317a22
Schroeder NO, Seeley MA, Hariharan A, Farley FA, Caird MS, Li Y. Utility of Postoperative Antibiotics After Percutaneous Pinning of Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2017;37(6):363-7. Doi:10.1097/BPO.0000000000000685
Aslan A, Konya MN, Ozdemir A, Yorgancigil H, Maralcan G, Uysal E. Open reduction and pinning for the treatment of Gartland extension type III supracondylar humeral fractures in children. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2014;9(2):79-88. Doi:10.1007/s11751-014-0198-7
Sabharwal S, Margalit A, Swarup I, Sabharwal S. The Pulseless Supracondylar Elbow Fracture: A Rational Approach. Indian J Orthop. 2020;55(1):47-54. Doi: 10.1007/s43465-020-00273-6
Fernandes F, Obregón PL. Características de vítimas de violência durante o período peri-pandêmico de Covid-19. BioSCIENCE. 2022;80(2):63-9. Doi: 10.55684/80.2.15